Fluid Mechanics lets you easily calculate compressible gas flow parameters for isentropic and normal shockwave flow.
Use Fluid Mechanics to check your Aerodynamics homework or use it to practice for the Professional Engineer exam’s compressible flow problems.
Features:
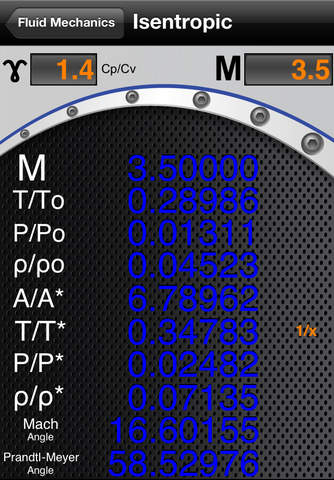
1. Isentropic flow Input parameters – gas constant ɤ (Cp/Cv,) and one of the following ** ten ** parameters:
• Mach number
• A/A*
(subsonic or supersonic)
• T/To
• P/Po
• ρ/ρo
• P/P*
• T/T*
• ρ/ρ*
• Mach angle
• Prandtl-Meyer angle
2. Isentropic flow Output parameters:
• Mach number
• A/A*
• T/To
• P/Po
• ρ/ρo
• P/P*
• T/T*
• ρ/ρ*
• Mach angle
• Prandtl-Meyer angle
3. Normal Shockwave flow Input parameters – gas constant ɤ (Cp/Cv), and one of the following ** seven ** parameters:
• Mach number upstream of shock (M1)
• Mach number downstream of shock (M2)
• P2/P1
• T2/T1
• ρ2/ρ1
• Po2/Po1
• P1/Po2
4. Normal Shockwave flow Output parameters:
• Mach number upstream of shock (M1)
• Mach number downstream of shock (M2)
• P2/P1
• T2/T1
• ρ2/ρ1
• Po2/Po1
• P1/Po2
5. Easily toggle between static-to-stagnation and stagnation-to-static ratios.
6. A users guide is provided within the in-program help.
7. Intuitive user interface.